A Lymph Node After Injection with Drug-Releasing Particles, Version #2
A Lymph Node After Injection with Drug-Releasing Particles, Version #2
Submitted by Christopher M. Jewell of the Irvine Lab at the Koch Institute
MIT Department of Biological Engineering, MIT Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Koch Institute at MIT
Christopher M. Jewell
Irvine Lab, Koch Institute
Confocal Micrograph
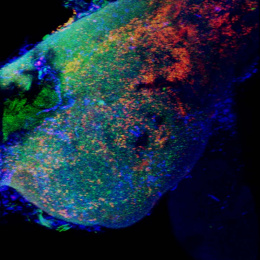
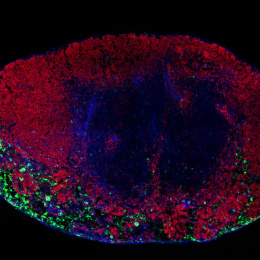
"Pictured is a lymph node excised from a mouse following intra-nodal injection of adjuvant-releasing polymer/biomaterial particles (green). The B cell and T cell compartments are shown in blue and red, respectively. We have developed a new biomaterials-based approach for establishing vaccine “depots” in lymph nodes – the site where antigen presenting cells interact with T cells and B cells to generate immune response during vaccination. This image (and similar images collected at regular intervals) revealed that polymer particles slowly release vaccines in the lymph node over time, significantly increasing vaccine persistence compared with conventional vaccines containing soluble/“free” components."